Purchasing Power Parity: Make it simple - ACCA FM Technical Article
- Tommy Leung
- Dec 31, 2017
- 3 min read
Updated: Mar 3, 2024
Purchasing Power Parity formula (PPP) is one important formula stated in ACCA Financial Management exam formulae sheet.
Many students confuse between Purchasing Power Parity and Interest Rate Parity. In fact, they are serving two different purposes.
Purchasing power parity is an important concept in international finance. It is a theory explaining the long term movement between two currencies.
Here we explain it in a simple way to help students to understand.
Formula
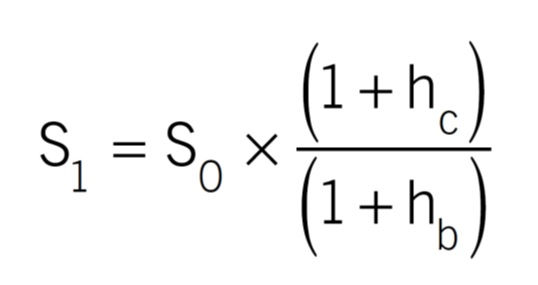
Where,
S1 = Expected spot rate in period 1
S0 = Current spot rate
hc = Expected inflation rate in country c
hb = Expected inflation rate in country b
Q: Which area of purchasing power parity relevant?
A: Purchasing power parity is relevant under risk management.
Q: What is purchasing power parity?
A: Purchasing power parity (PPP) is an economic theory that states that the exchange rate between two currencies is equal to the ratio of the currencies' respective purchasing power.
Q: What does purchasing power parity indicate?
A: PPP formula indicates that a country with relatively higher expected inflation will be suffered from currency depreciation against another country with lower expected inflation.
Q: What does purchasing power parity apply?
A: With strong economic theory support, PPP is a widely accepted tool in forecasting an exchange rate movement between two currencies in long run.

Illustration
Application of the knowledge learnt is always challenging but given you could spend time to do past paper question, it is not that difficult to master the skill.
An example is from ACCA Financial Management Specimen paper 2016 while part of the question is asking Purchasing Power Parity Theory.

Acknowledgement: The question is extracted from past ACCA exam paper which is for our explanation only.
The question asks which statement(s) is/are correct for both Purchasing Power Parity Theory and Interest Rate Parity Theory.
Here we focus on Purchasing Power Parity Theory.
Statement 1 is about the theory holds in long term rather than short term.
Purchasing Power Parity Theory holds in long term but not in short term exchange fluctuations because short term changes are caused by a lot of factors including psychological and economic reasons.
Statement 1 is correct for PPP.
Statement 2 says whether the theory explains the exchange rate changes reflecting the cost of living in two countries.
The core of Purchase Power Parity Theory is inflation rate difference between two countries. It explains the gap in cost of living in two countries would result in exchange rate changes.
Statement 2 is correct for PPP.
Statement 3 says a currency of a country with higher inflation rate will weaken against the other currency.
As described above, Purchasing Power Parity indicates that a country with relatively higher expected inflation will be suffered from currency depreciation against another country with lower expected inflation.
So, Statement 3 is correct for PPP.
However, Interest Rate Parity Theory does not agree on Statement 2 and Statement 3, so the correct answer here is Option D, 1 only.

Conclusion
A popular magazine conducts a research annually based on a world recognized fast food restaurant hamburger price.
The study shows the hamburgers are sold in different prices in different countries while the magazine published this "hamburger index" showing cost of living level in the world.
It is one of good examples to understand Purchasing Power Parity Theory.
As said, Purchasing Power Parity Theory is one of important topic in risk management on foreign exchange rate. It helps to explain foreign exchange rate fluctuations.
In the exam, you are advised to know when to use PPP, such as forecasting future spot exchange rate.
If you would like to go deep in this topic, just check our Practice Question and Mock Exam for more questions.
Follow us on our Facebook Page to have update:





Σχόλια